Cloud-Based Quantum Computing: A Complete Guide
Introduction
Quantum computing has long been associated with futuristic laboratories, complex physics, and hardware accessible only to elite research institutions. However, the rise of cloud-based quantum computing is rapidly changing this narrative. By combining quantum processors with cloud infrastructure, technology providers are making quantum computing accessible to developers, researchers, and businesses around the world – without the need for expensive hardware or specialized facilities.
Definition
Cloud-based quantum computing is a model of quantum computation in which users access quantum processors remotely via the internet, rather than owning and operating quantum hardware locally. Through cloud platforms, researchers and developers can run quantum algorithms, experiment with quantum circuits, and integrate quantum resources with classical computing systems on demand, reducing cost and technical barriers while enabling broader access to emerging quantum technologies.
Understanding Quantum Computing in Simple Terms
Traditional computers use bits, which exist as either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, use qubits, which can exist in a superposition of both 0 and 1 simultaneously. In addition, qubits can become entangled, meaning the state of one qubit can depend on the state of another, even across distance.
These properties allow quantum computers to process certain types of problems – such as optimization, cryptography, molecular simulation, and complex probabilistic modeling – far more efficiently than classical systems. However, quantum hardware is extremely sensitive, requiring ultra-cold temperatures, vibration isolation, and advanced error-correction techniques. This makes on-premises quantum systems impractical for most organizations.
What Is Cloud-Based Quantum Computing?
Cloud-based quantum computing refers to accessing quantum processors remotely through cloud platforms, much like virtual machines or GPUs are accessed today. Instead of owning and maintaining quantum hardware, users interact with quantum systems via APIs, software development kits (SDKs), and web interfaces.
Cloud providers host quantum computers in controlled environments and allow users to submit quantum programs, run experiments, and retrieve results over the internet. This model removes the barriers of cost, complexity, and infrastructure, enabling broader experimentation and innovation.
Key Components of Cloud-Based Quantum Platforms
Most cloud-based quantum ecosystems consist of three core layers:
- Quantum Hardware
These include superconducting qubits, trapped ions, photonic systems, or neutral atoms. Different providers explore different hardware approaches, each with unique strengths and limitations. - Quantum Software Stack
This layer includes programming languages, compilers, simulators, and error-mitigation tools. Popular frameworks allow developers to write quantum circuits using high-level abstractions, often integrated with classical programming languages like Python. - Cloud Infrastructure and Access
Secure cloud services manage job scheduling, authentication, data handling, and hybrid workflows that combine classical and quantum computation.
Together, these layers allow users to focus on problem-solving rather than hardware maintenance.
Why Cloud-Based Quantum Computing Matters
1. Democratized Access
Cloud platforms allow startups, universities, and independent developers to experiment with quantum computing without massive capital investment. This accessibility accelerates learning and innovation across industries.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Users can run small experiments today and scale up as hardware improves. Cloud providers continuously upgrade quantum processors, allowing users to benefit from advances without changing their codebase.
3. Hybrid Computing Models
Many real-world applications require a combination of classical and quantum computation. Cloud environments make it easier to orchestrate hybrid workflows, where classical processors handle data preparation and post-processing while quantum hardware tackles computationally hard subproblems.
4. Faster Research and Development
By removing logistical barriers, researchers can iterate faster, test algorithms on real quantum hardware, and share results globally. This collaborative environment is essential for a technology still in its early stages.
Real-World Use Cases
Although quantum computing is still maturing, cloud-based access is already enabling practical experimentation in several domains:
- Drug Discovery and Materials Science
Quantum systems can model molecular interactions at a level of precision difficult for classical computers, potentially accelerating the discovery of new drugs and materials. - Financial Modeling and Optimization
Portfolio optimization, risk analysis, and fraud detection involve complex probability calculations that may benefit from quantum algorithms. - Supply Chain and Logistics
Quantum optimization techniques can help solve routing, scheduling, and resource allocation problems more efficiently. - Machine Learning and AI
Quantum machine learning is an emerging field exploring how quantum systems can enhance pattern recognition, clustering, and data sampling.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, cloud-based quantum computing faces several challenges:
Hardware Limitations:
Current quantum computers are noisy and error-prone, with a limited number of qubits. This era is often referred to as Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) computing.
Algorithm Maturity:
Many quantum algorithms are still theoretical or require fault-tolerant systems that do not yet exist at scale.
Skill Gap:
Quantum computing requires knowledge of linear algebra, quantum mechanics, and new programming paradigms. Cloud platforms help, but the learning curve remains steep.
Security and Data Privacy:
Sending sensitive data to cloud-hosted quantum systems raises concerns about confidentiality and compliance, especially for regulated industries.
The Role of Major Cloud Providers
Leading cloud vendors are investing heavily in quantum research and cloud delivery models. They offer quantum simulators for learning, real quantum hardware for experimentation, and integrated development environments that bridge classical and quantum workflows.
This competition is driving rapid progress, standardization efforts, and the development of open-source tools, all of which benefit the broader ecosystem.
The Future of Cloud-Based Quantum Computing
As hardware improves and error-correction advances, cloud-based quantum computing is expected to move from experimental to practical. In the coming years, we can expect:
- Larger and more stable quantum processors
- Improved quantum-classical integration
- Industry-specific quantum applications
- Greater standardization in quantum software development
Rather than replacing classical computing, quantum systems will act as powerful accelerators for specific problem types – delivered seamlessly through the cloud.
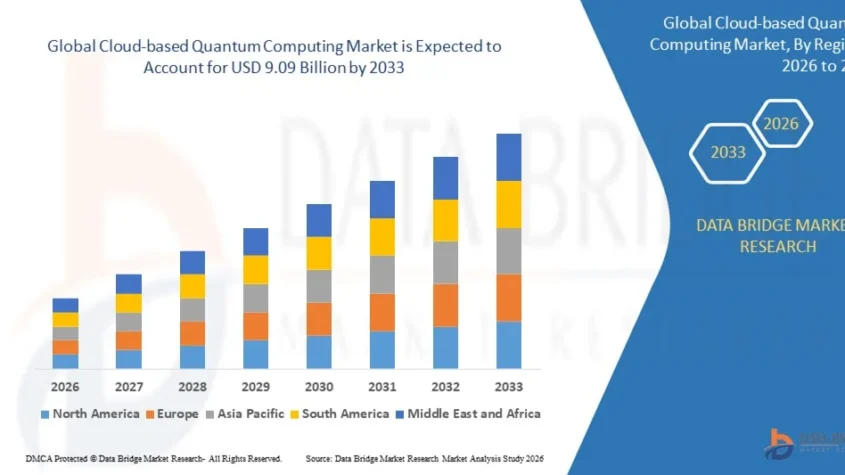
Growth Rate of Cloud-based Quantum Computing Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the cloud-based quantum computing market was estimated to be worth USD 1.12 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.81% to reach USD 9.09 billion by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cloud-based-quantum-computing-market
Conclusion
Cloud-based quantum computing represents a critical bridge between cutting-edge quantum research and real-world application. By abstracting away hardware complexity and providing global access, the cloud is enabling a new generation of developers and researchers to explore quantum possibilities today.
Easy tips and tricks to clean your sofa at home
The sofa is the center of your living space. Your sofa is a place where you can relax, ent…